About This Reference
This page visualizes the key audio features that librosa can extract from music and audio files. Each visualization was generated from a 5-second trumpet sample using the analysis script.
Location: music-analysis/audio_analysis.py — run with your own audio files.
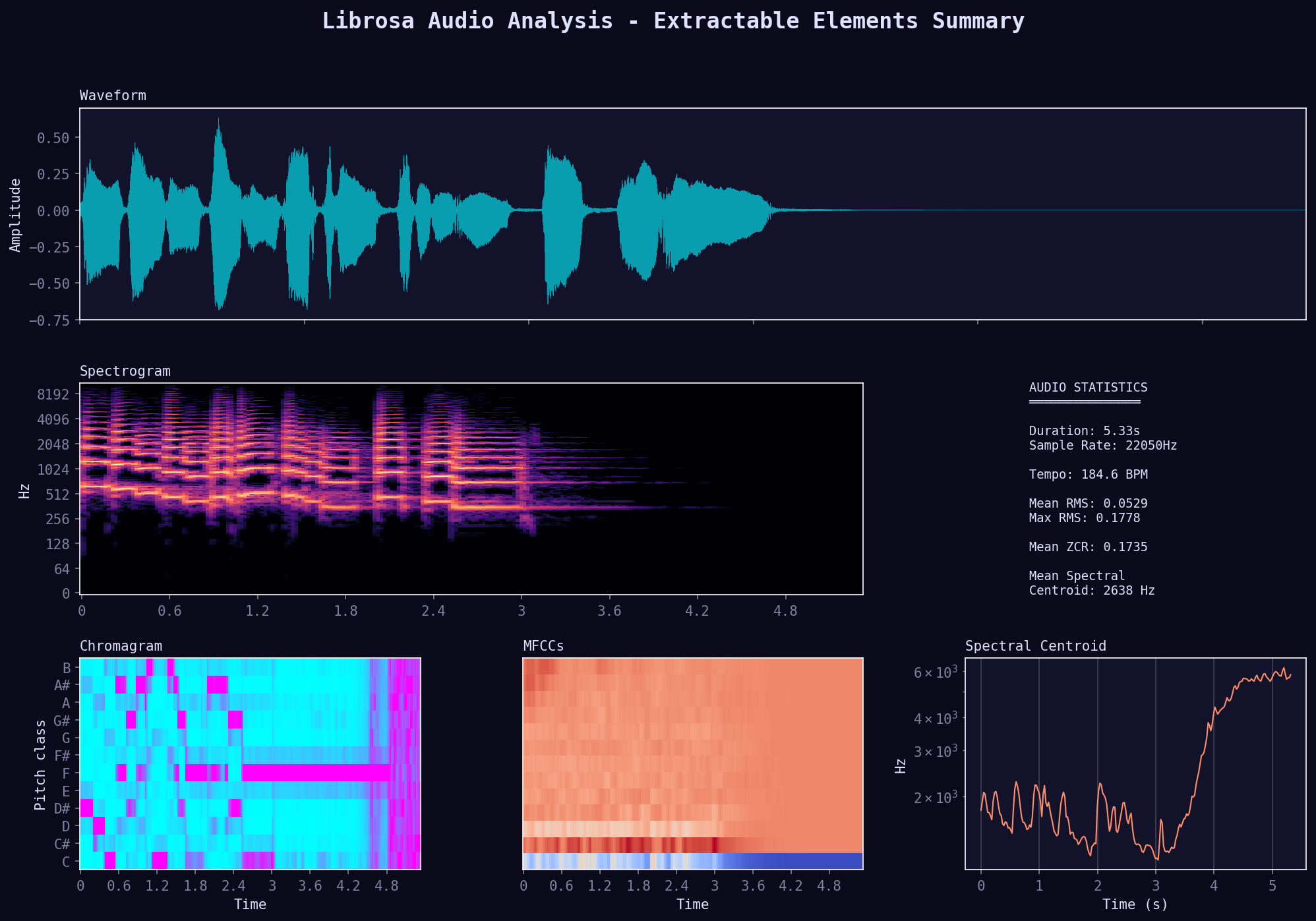
Feature Summary Dashboard
Complete overview showing all extractable features in one view. Includes waveform, spectrogram, chromagram, MFCCs, and spectral centroid with audio statistics.
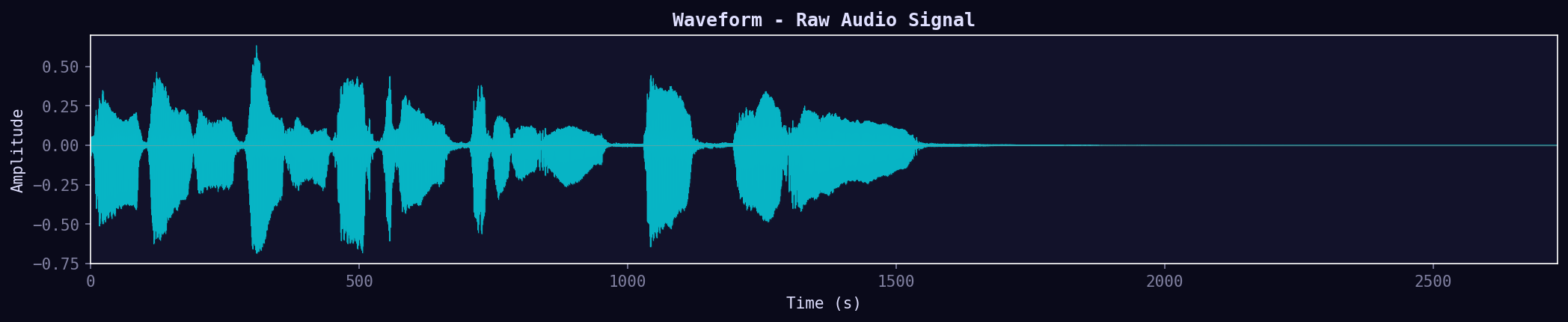
01. Waveform
Raw amplitude over time. The fundamental representation of audio — amplitude vs time. Shows the "shape" of the sound wave.
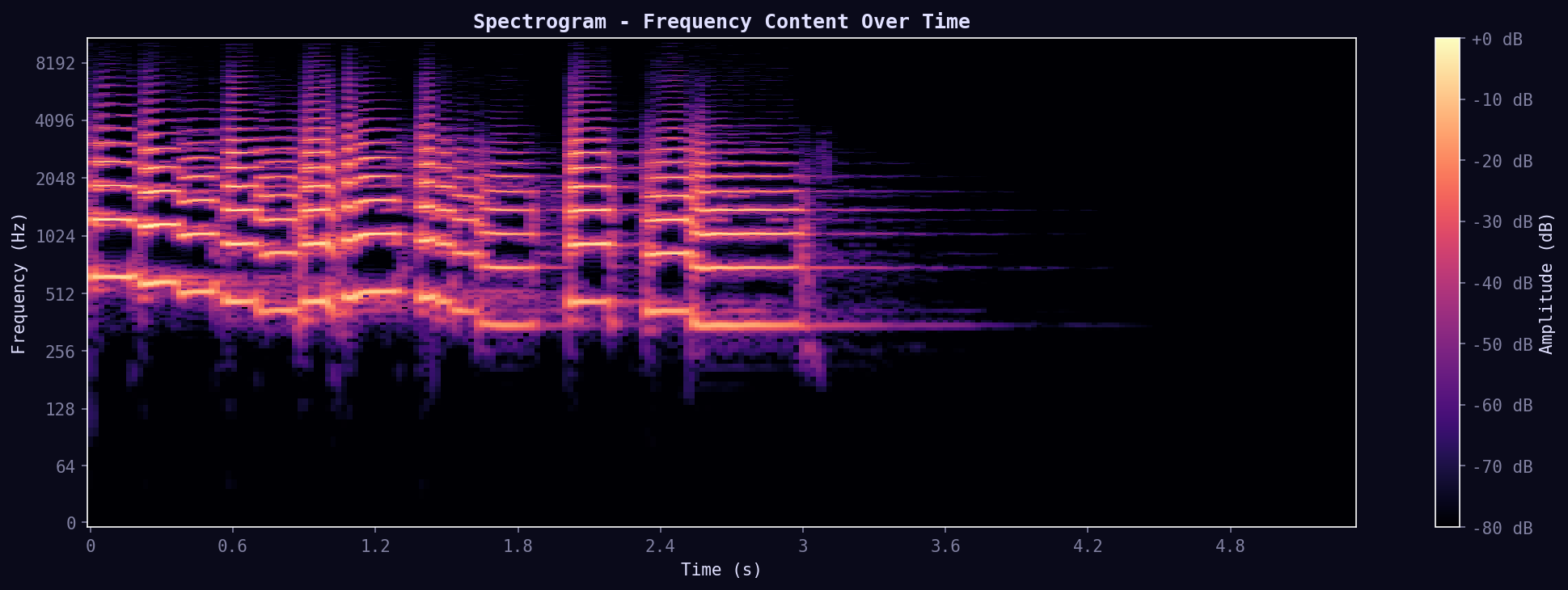
02. Spectrogram
Frequency content over time. Shows which frequencies are present at each moment. Brighter colors = more energy. Reveals harmonics, overtones, and spectral structure.
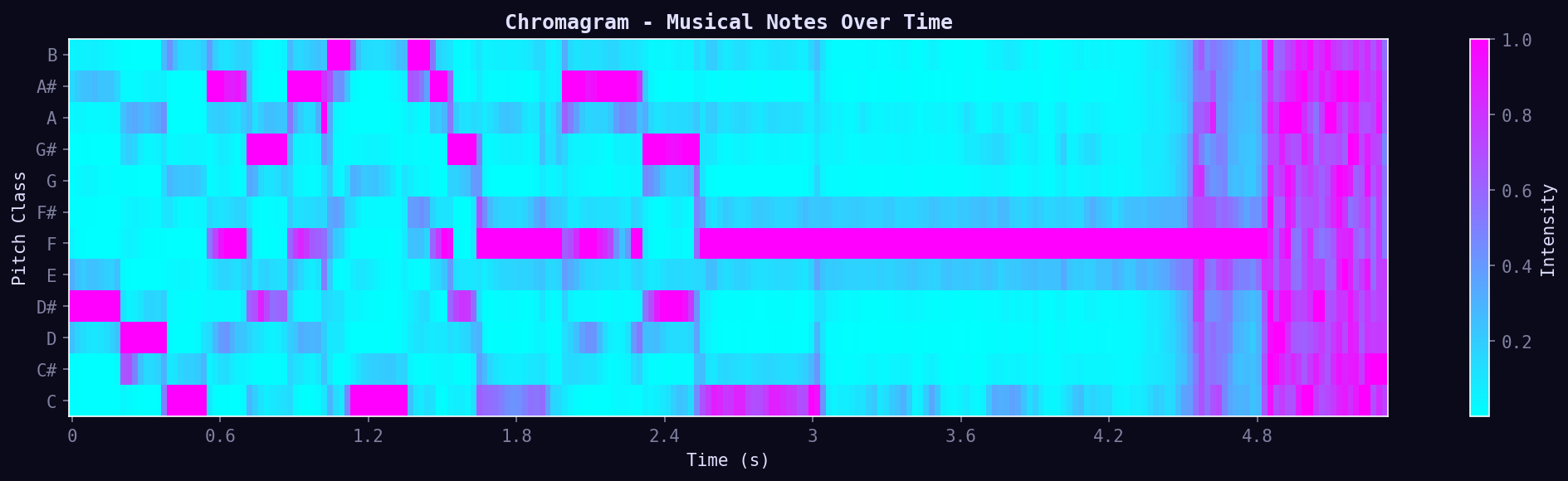
03. Chromagram
Musical pitch classes over time. Shows which notes (C, C#, D, etc.) are present. Invariant to octave — C4 and C5 both appear as "C". Useful for chord detection and key analysis.
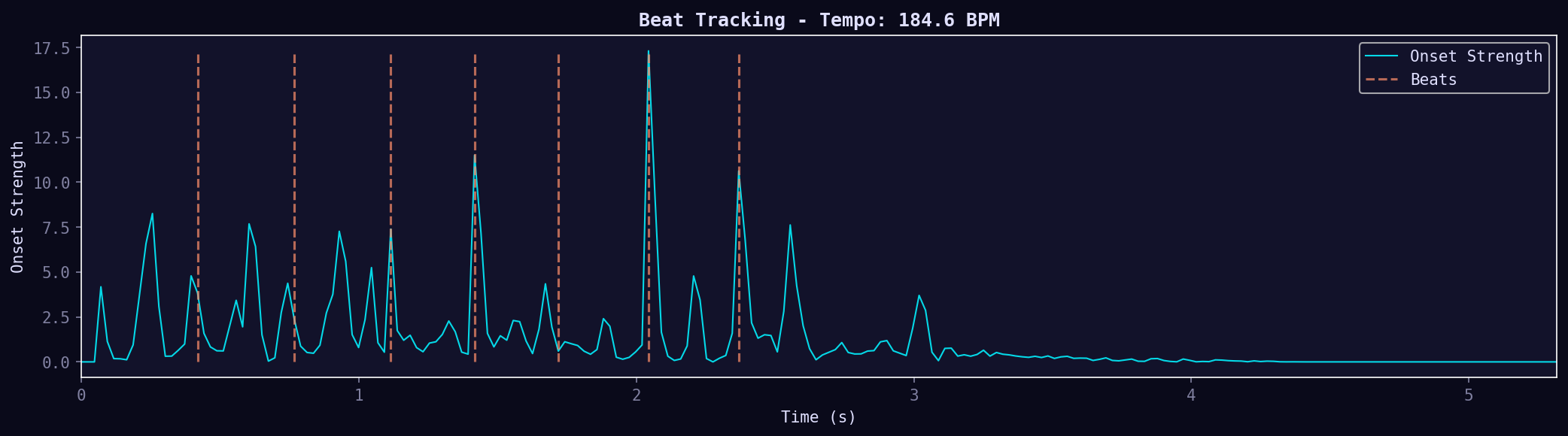
04. Beat Tracking
Tempo estimation and beat detection. Shows onset strength (energy spikes) and detected beat positions. Output: BPM and beat timestamps for rhythm analysis.
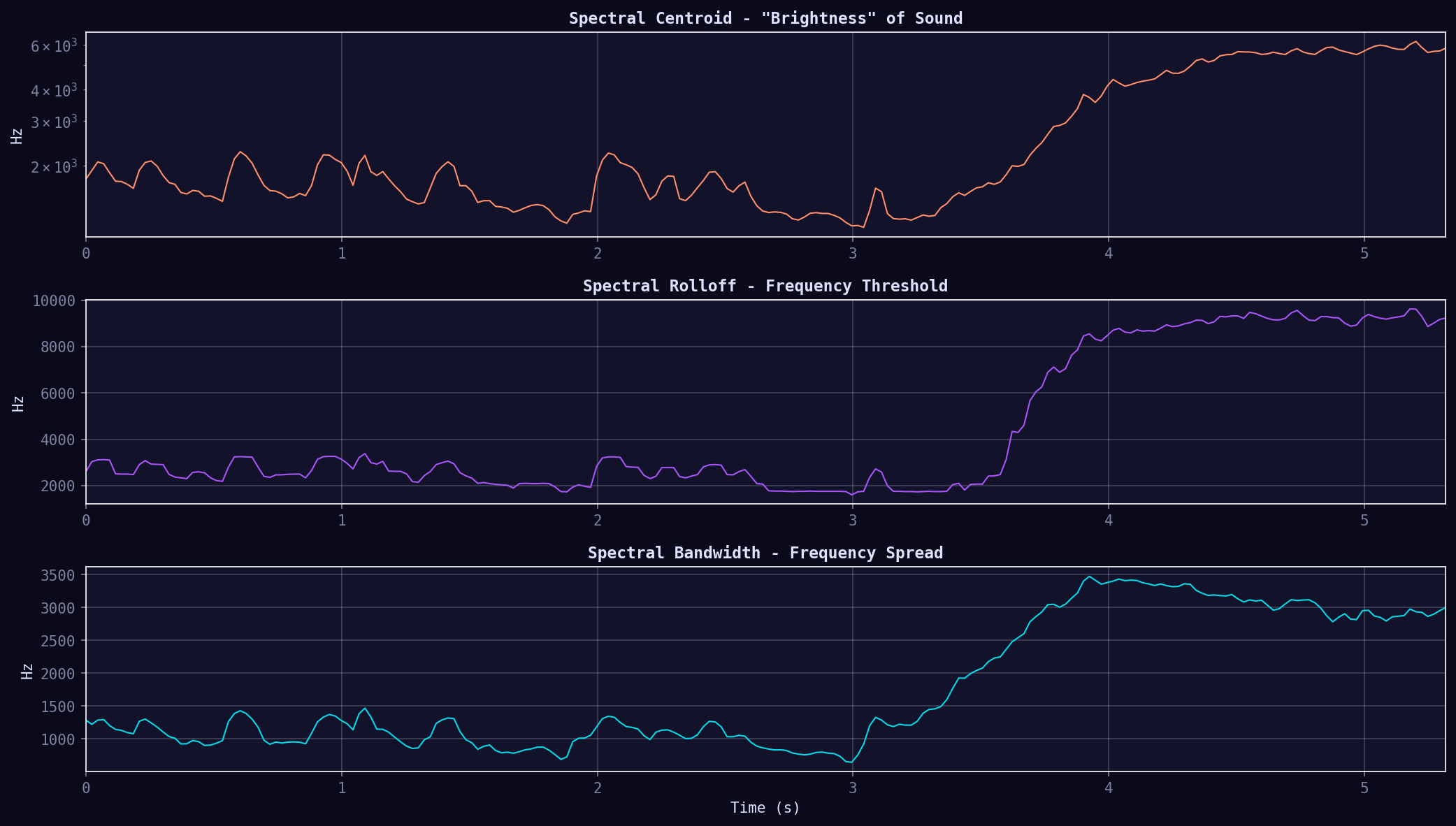
05. Spectral Features
Three key spectral descriptors: Centroid ("brightness"), Rolloff (frequency threshold), and Bandwidth (spread). Describe the timbral quality and frequency distribution.
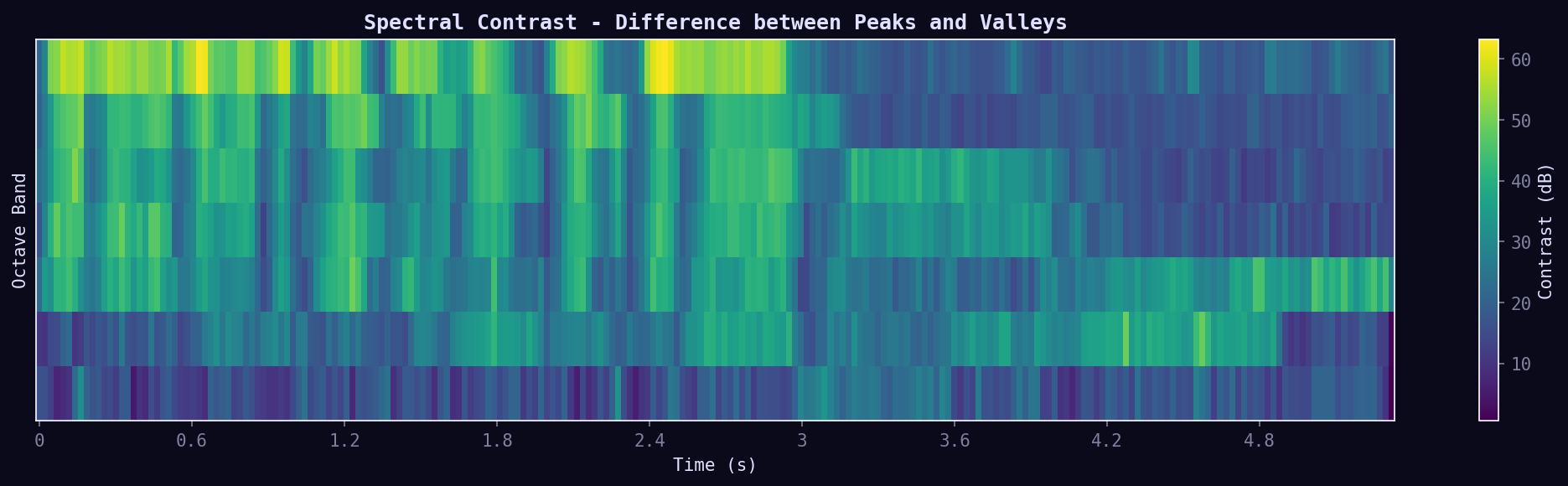
06. Spectral Contrast
Difference between spectral peaks and valleys per octave band. High contrast = clear harmonic structure; Low contrast = noisy/flat spectrum. Good for genre classification.
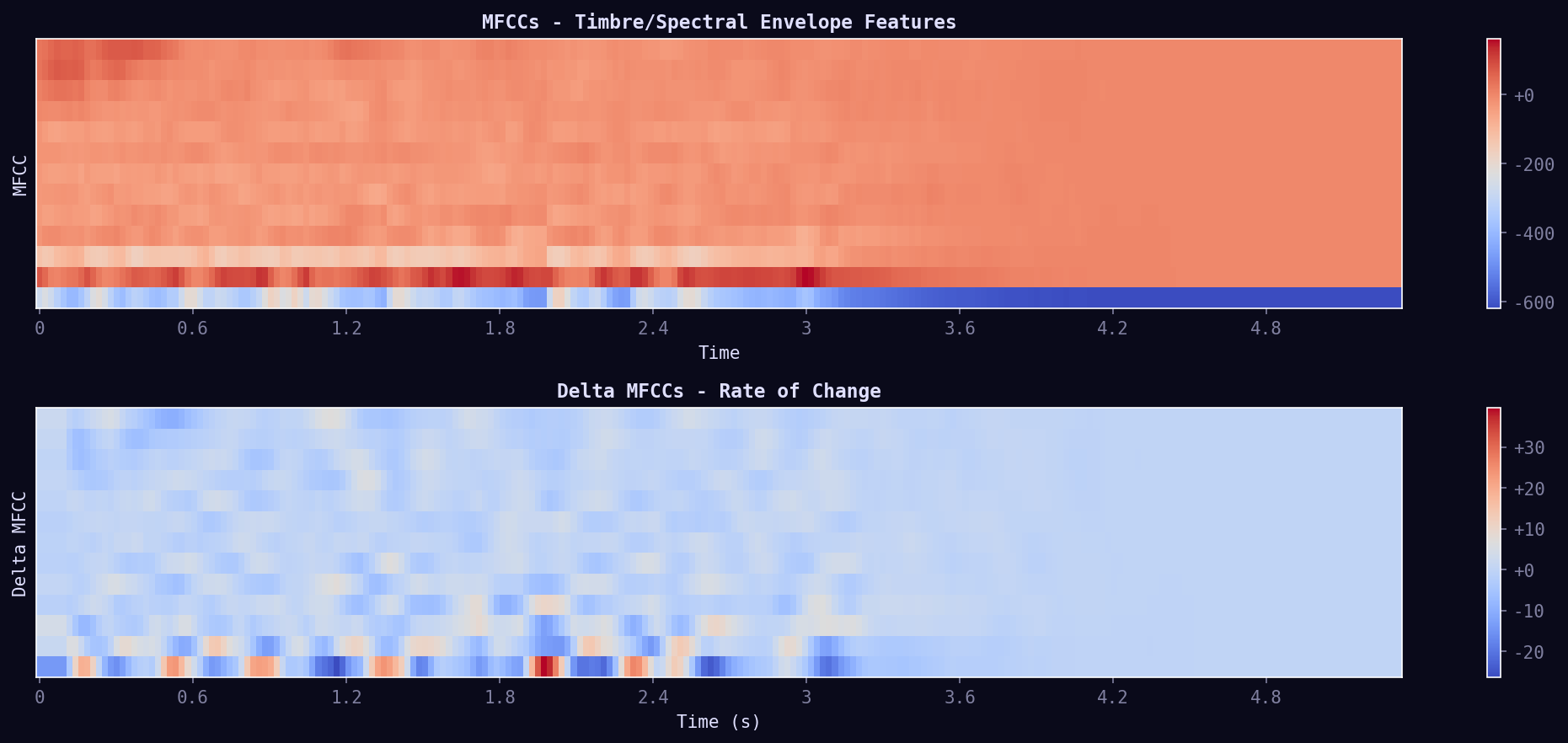
07. MFCCs
Mel-Frequency Cepstral Coefficients — the "fingerprint" of timbre. Captures how we perceive sound (human hearing is logarithmic). Used in speech recognition, music genre classification, and instrument identification.
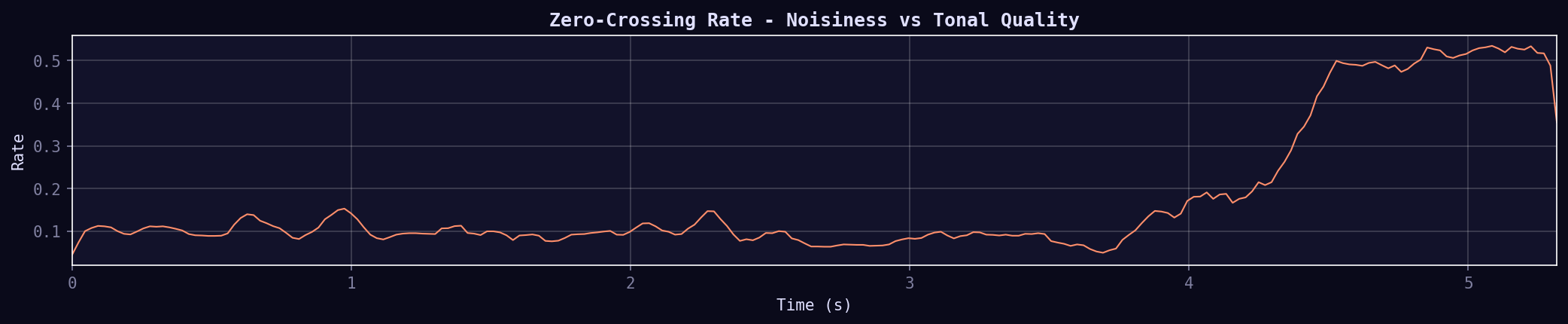
08. Zero Crossing Rate
Rate at which the signal changes sign. High ZCR = noisy/percussive sounds; Low ZCR = tonal/sustained sounds. Simple but effective for distinguishing speech vs music, or drums from melody.
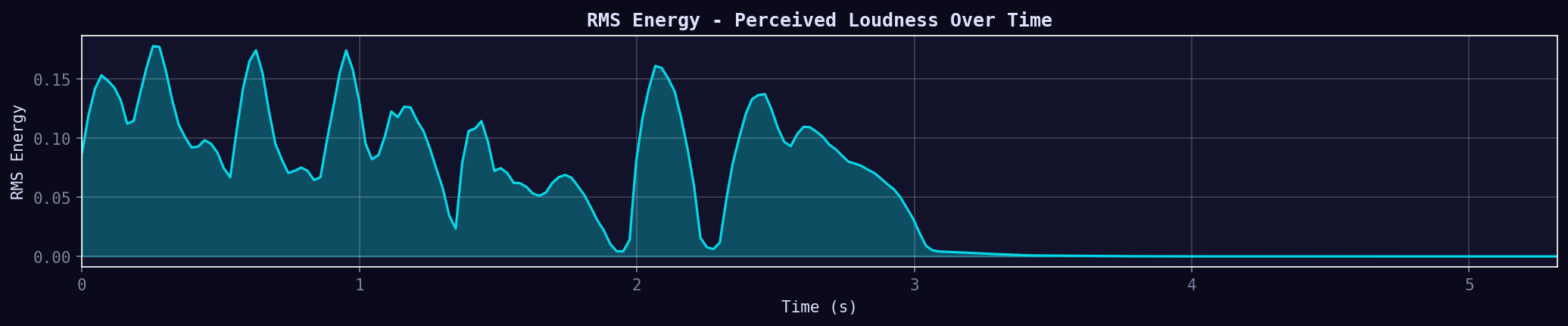
09. RMS Energy
Root Mean Square energy — perceived loudness over time. Smooths the amplitude to show overall energy envelope. Useful for detecting silence, loud sections, or for visualization.
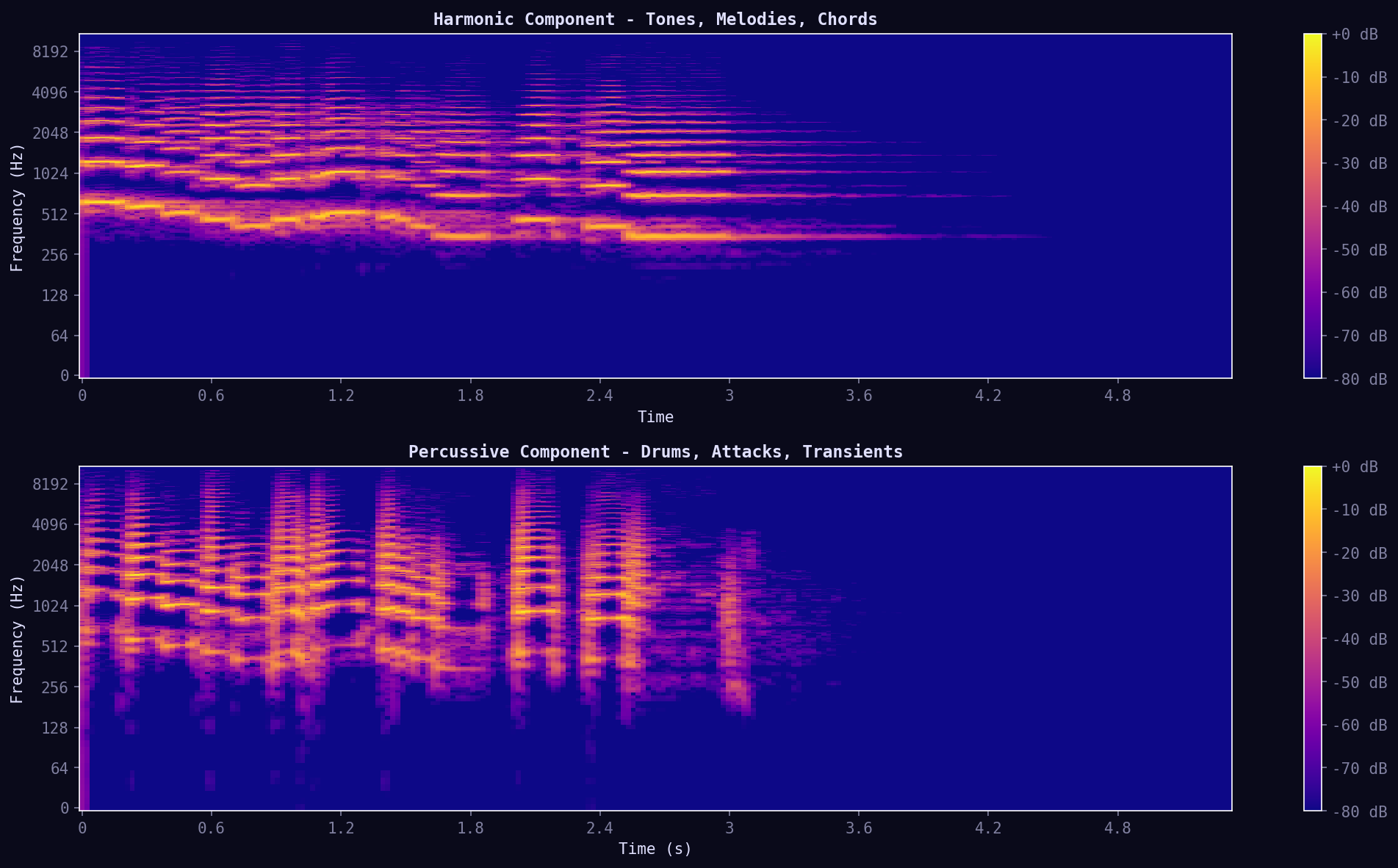
10. Harmonic/Percussive Separation
Source separation using HPSS (Harmonic-Percussive Source Separation). Separates sustained tones (melody, chords) from transient attacks (drums, plucks). Enables isolated analysis of melody or rhythm.
| Feature | Use Case | Type |
|---|---|---|
| Waveform | Basic visualization, amplitude analysis | Time Domain |
| Spectrogram | Frequency analysis, harmonic detection | Frequency Domain |
| Chromagram | Chord detection, key analysis | Musical |
| Beat Tracking | Tempo estimation, rhythm section analysis | Rhythm |
| Spectral Features | Timbre description, brightness analysis | Timbre |
| MFCCs | Speech recognition, genre classification | Timbre |
| Zero Crossing | Noise vs tone discrimination | Time Domain |
| RMS Energy | Loudness analysis, silence detection | Time Domain |
| HPSS | Source separation, melody vs drums | Separation |